VVT20 - Perfect contact thermal coupling on non-matching elements
| Solution | Test case |
|---|---|
| Finite volume method | SVTEST25 |
| Finite element method | SVTEST251 |
Description
This validation case examines a perfect contact between two plates with non-matching grids without mesh mating elements. It compares the steady-state nodal temperature of the faces that are in contact with each other.
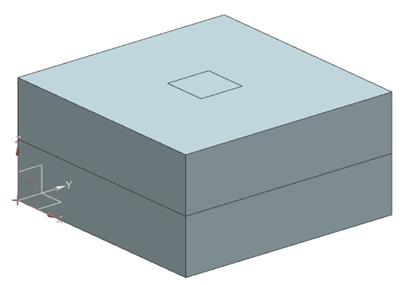
Geometry
The geometry consists of two similar plates with a length and width of 100 mm, and a height of 25 mm each. The plates are in contact with each other.
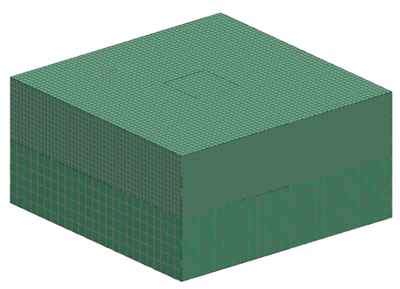
Simulation model
This model uses the Advanced Thermal solution type.
The swept mesh of two plates is made of hexahedral elements. The element size of the fine mesh plate and the coarse mesh plate is 2.5 mm and 5 mm, respectively. The interface elements of the coplanar faces are not matching.
The following cylinders properties are used:
- Material: Aluminum_6061
- Mass density: ρ = 2711 kg/m3
- Specific heat at constant pressure: Cp = 896 J/kg·°C
The following boundary conditions are applied:
- Thermal Coupling-Advanced: Perfect Contact between the fine mesh plate face and the coarse plate face. Primary selection is the fine mesh plate face and the secondary selection is the coarse mesh plate face.
- Temperature constraint on the coarse mesh plate face with the value of 500 °C.
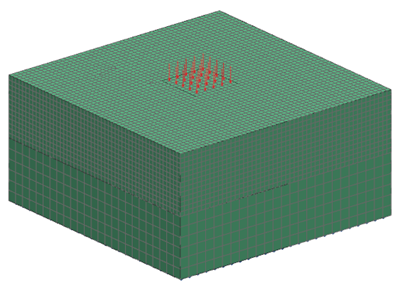
- Thermal Loads: Heat Load on the square surface with a length of 10 mm in the middle of the fine mesh plate, as shown on the following figure. The value of head load is 500 W.
The default solver parameters are selected.
Theory
Perfect thermal contact between a solid surface A and a solid surface B occurs when the temperature and heat fluxes of the mating surfaces are equal.
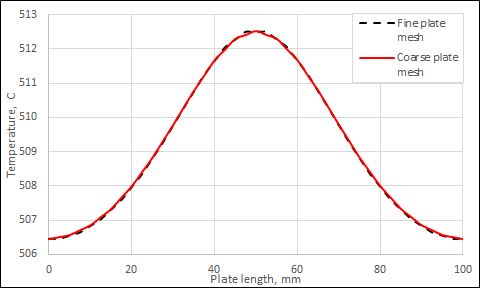
Results
The following figure compares the computed nodal temperatures of the fine mesh and coarse mesh plates on the ZY cutting plane for the finite volume method.