K-omega turbulence model
The flow solver applies specific boundary conditions for the k-omega turbulence model on both smooth and rough walls, using standard and hybrid wall functions to calculate turbulent kinetic energy and other parameters.
The flow solver uses the following values for the wall resolved k-omega turbulence model boundary conditions on a smooth wall:
The boundary conditions for the wall resolved k-omega turbulence model on a rough wall are given by:
where k+s is the equivalent sand grain roughness height in wall units and is calculated as follow:
Standard wall function
For k-omega turbulence model that uses the standard wall function, the flow solver calculates the boundary conditions similarly as to the k-epsilon turbulence model, with exception that instead of ε value, it uses ω value:
where:
For the k equation, the convective and diffusive fluxes on the wall boundary are set to zero.
Hybrid wall function on smooth walls
The turbulent kinetic energy is zero on the wall.
The near-wall solution for ω is defined as described in [36] and can be written in the wall units as follow:
where
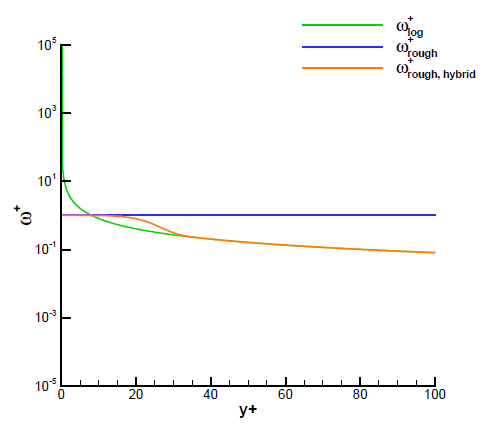
Hybrid wall function on rough walls
Turbulent kinetic energy is set to zero on rough walls. The boundary condition for ω is a blend of the resolved rough wall value ω+rough and the log layer value ω+log. Unlike the smooth resolved boundary value, ω+vis, the rough wall boundary value, ω+rough, is independent of y+.