Wall functions with roughness effect
The roughness effect is incorporated in wall functions with parameters such as the specified equivalent sand grain roughness.
In addition to the linear relation in the viscous sublayer, the wall function can include the roughness effect as follows:
- ks is the specified equivalent sand grain roughness.
- u* is the shear velocity. For more information, see Mixing length turbulence model.
The roughness effect shifts the log-law, but does not affect the slope.
The equation for the standard wall function with roughness effect is as follow:
Plots of wall function dimensionless velocity, U+ for varying dimensionless roughness is shown in the following figure. For reference, the smooth wall log-law and the linear function are also plotted as solid lines.
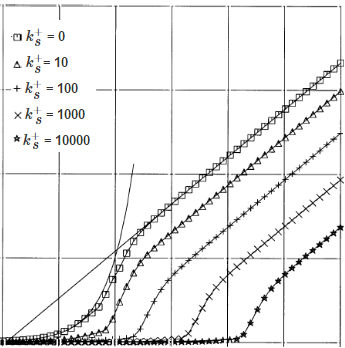
The equation for the hybrid wall function with roughness effect is as follow:
- C1 is an empirical constant that depends on the dimensionless roughness height k+s.
Reichardt's law that takes into account the roughness effect:
FReimix blends Reichardt's law with classical log-law as follows:
- C2 is an empirical constant that depends on the dimensionless roughness height k+s.
Spaldings law is given by the following inverse formula:
