How to define a thermostat based on a temperature difference between two elements?
This article provides two methods for defining a thermostat based on a temperature difference between two elements.
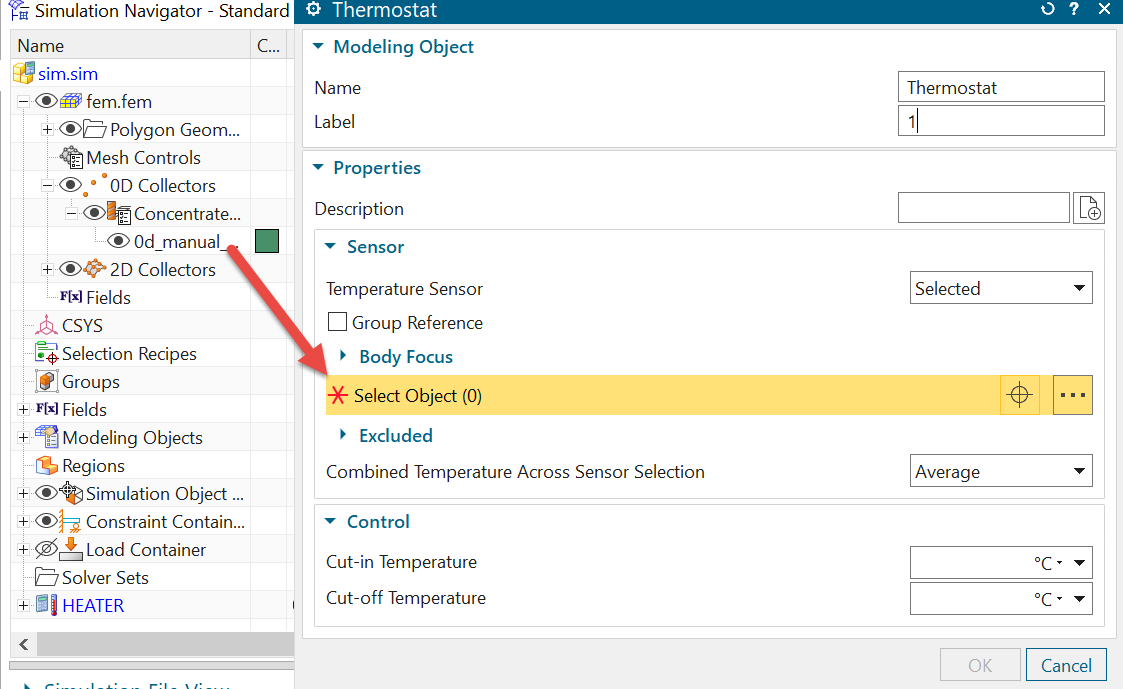
Using a Thermostat modeling object
- Create named points on the geometry at the locations where you want to monitor temperatures, for example P1 and P2. On the Home tab, in the Tool group, click Point. Then, right-click the created point and select Properties. On the General tab, in the Name box, type P1. Repeat this process for the second point.
- Create a 0D element that is not connected to anything else in the model.
- Constrain the 0D temperature to be a function of the named points. For
example, use this expression:
(TEMP("P1")-TEMP("P2"))/1[dC]
- Use the 0D element as a sensor for the thermostat.
Using a thermal load
- Create named points on the geometry at the locations where you want to monitor temperatures, the same way as explained in the first method.
- Create a Thermal Load simulation object with an
expression that controls the heat load based on the temperatures at the
named points: For example, use the expression:
if ((TEMP("P1")-0[C])/1[dC]) < ((TEMP("P2")-0[C])/1[dC]) then 1 else 0
The second method, however, does not provide the data that a thermostat function provides, such as actuations or average power.
