Finite element mesh
To solve conduction heat transfer in a solid domain, a mesh is essential when using the finite element method.
The thermal solver applies several types of 2D and 3D mesh elements. For each element type, shape functions are required to obtain a discrete system of equations. Computation of the discrete equations are simplified by a coordinate transformation known as mapping.
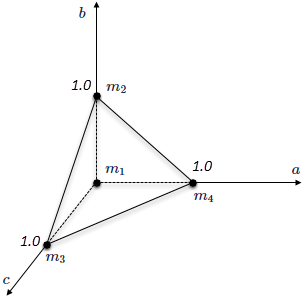
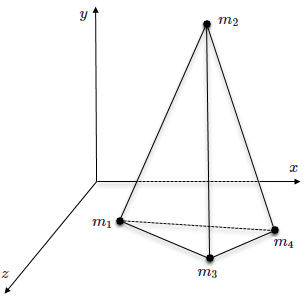
The thermal solver uses a coordinate transformation to map each node of an element in the original coordinate system to a corresponding node in the transformed coordinate system. The examples show each node, mj of an element in the original Cartesian (x, y, and z) coordinate system and its representation in the transformed (a, b, and c) coordinate system [6].
This example shows an element in the original Cartesian coordinate system.
Here the element is in the transformed coordinate system.